Overview of this database
This database is a comprehensive database that provides manually curated associations between metabolic syndrome and non-coding RNAs, including microRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs. In the current release, this database provides 1505 manually curated associations between 1289 miRNAs, 200 lncRNAs, and 16 circRNAs and metabolic syndrome traits, including abdominal obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipi-daemia and hypolipoproteinaemia across 6 species from more than 4000 published literatures.
This database offers 1) Browse and 2) Search pages as well as downloadable lists of metabolic syndrome-ncRNAs associations. 3) This database offers a submission page for users to submit novelty validated associations. Once the submission approved by our review committee, the record(s) will be involved in the update release. 4) The Statistics page contains statistical analysis visualizations of all data in the database and the validation methods used to validate them. 5) The Interaction network page provide users with a data visualization interface that makes it easy to see the connections between data.
Browse help
In the Browse page, users can browse the metabolic syndrome-ncRNAs associations by clicking a specific metabolic syndrome trait, microRNA, lncRNA or circRNA. Then, users can filter the results by selecting a specific ncRNA category, species, experimental method, and a corresponding results table will display.
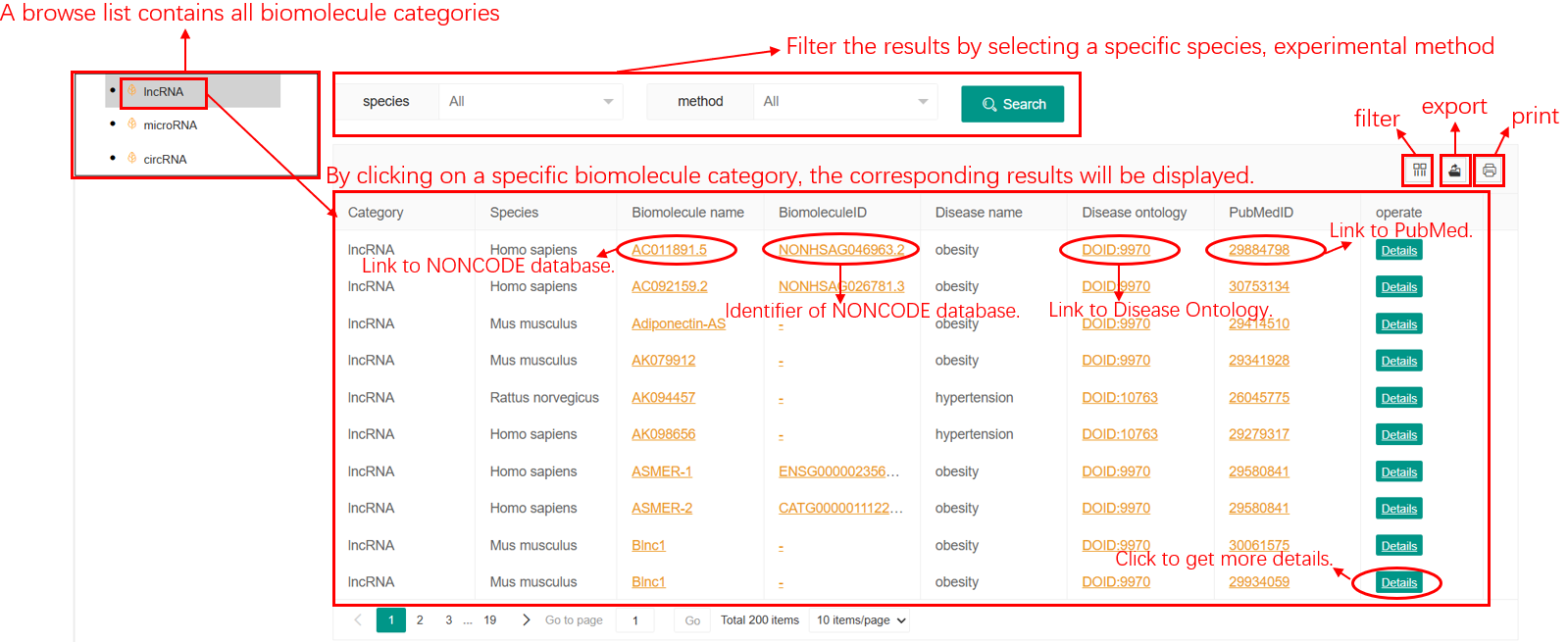 Figure 1. Browse Page
Figure 1. Browse Page
Search help
In the Search page, users can search by a specific metabolic syndrome trait name or a microRNA, lncRNA or circRNA name. Users can also search by inputting both metabolic syndrome trait name and a microRNA, lncRNA or circRNA name. ncRNA2MEtS 2.0 provides an option in the search page that enables users to filter associations by specific experimental methods. ncRNA2MetS 2.0 offers a fuzzy search function for the entries by the full or partial names of ncRNAs and/or metabolic syndrome trait.
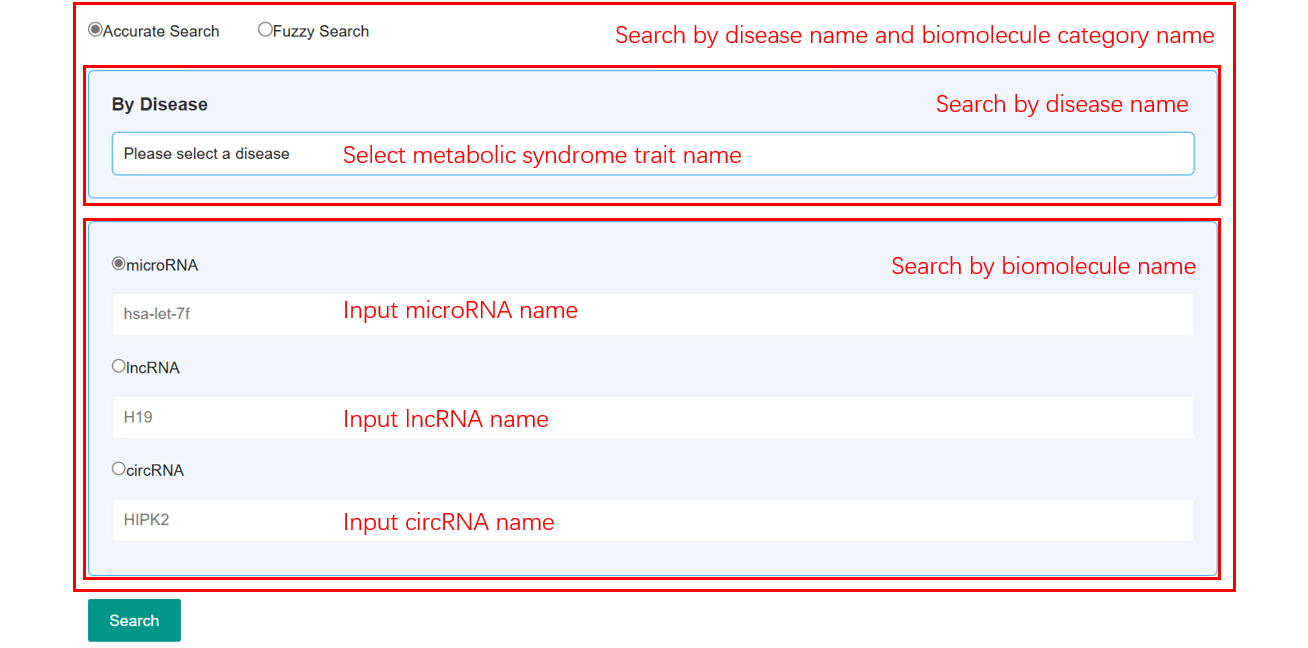 Figure 2. Search Page
Figure 2. Search Page
Search result
There is a data table shows when users initiate a search request. Each entry contains the information about ncRNAs (microRNA, lncRNA or circRNA), metabolic syndrome traits and their relationships, including ncRNA category, Species, ncRNA name, disease name, PubMed ID and details. Users can click on the "Download Search Result" button to download the data table and the "details" button to view a comprehensive information about this entry.
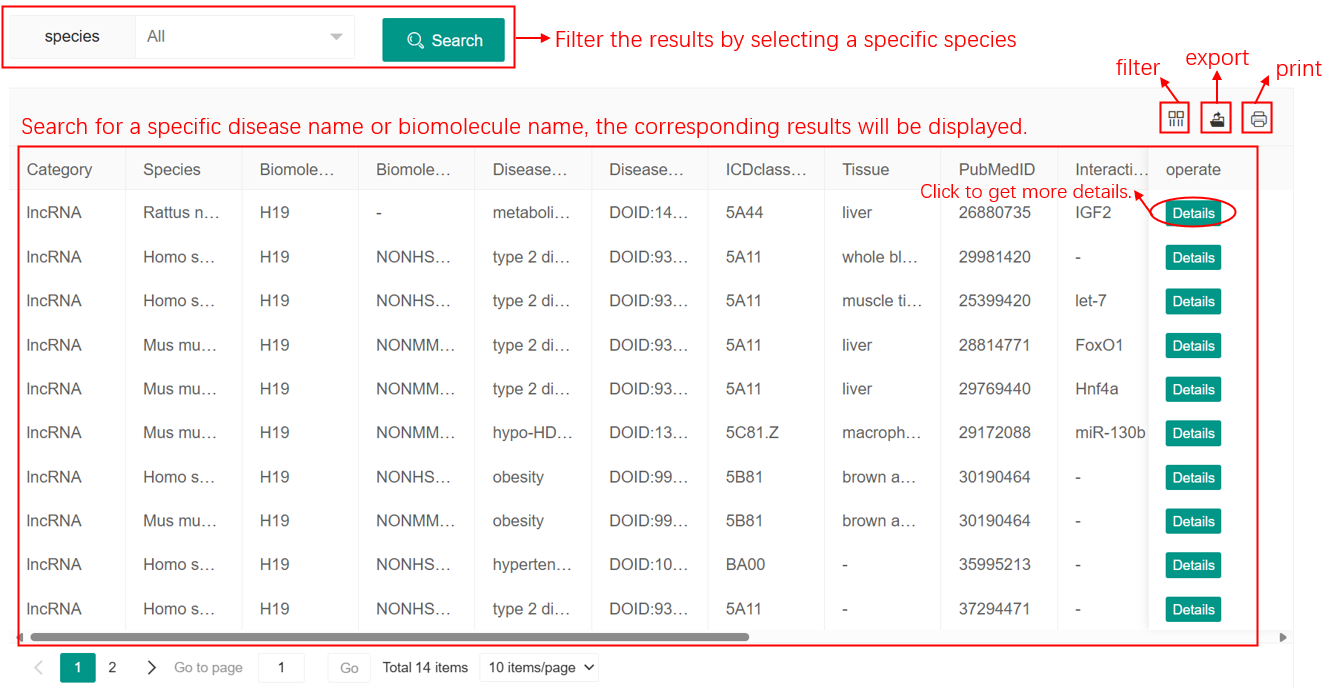 Figure 3. Search Result Page
Figure 3. Search Result Page
Details
To get detailed information on ncRNA2MetS 2.0 needs to click on the details button of the data table. It will open another page to show a comprehensive information of the selected entry.
Submit
In the submission page, users can submit data or data files to us, and in the submission module, users can enter the data information they want to submit in turn according to the system form prompts, and click Submit to upload to us if they meet the form submission requirements. If you make a mistake during the period, you can click Reset to re-enter. If you want to upload a large amount of data, the module also supports uploading and submitting in the form of files.
Statistics
On the statistical analysis page, users can intuitively see the statistical analysis of all non-coding RNA data based on metabolic syndrome and the results, such as the number of non-coding RNAs in the system and the number of non-coding RNAs in each category, and can also view the proportion of data under different conditions, including diseases, species or biomolecular species and research on the number of different species, the number of associated RNAs for various types of diseases, number of relevant papers published on PubMed from 2011 to August 2024, comparisons with other databases.
Interaction
When the user enters the interactive network page, after the user enters the interactive network page, he clicks on the biomolecule he wants to view according to the biomolecule category, and the biomolecule he wants to view is displayed in the right side of the page in the form of a line connection with the gene he is targeting.
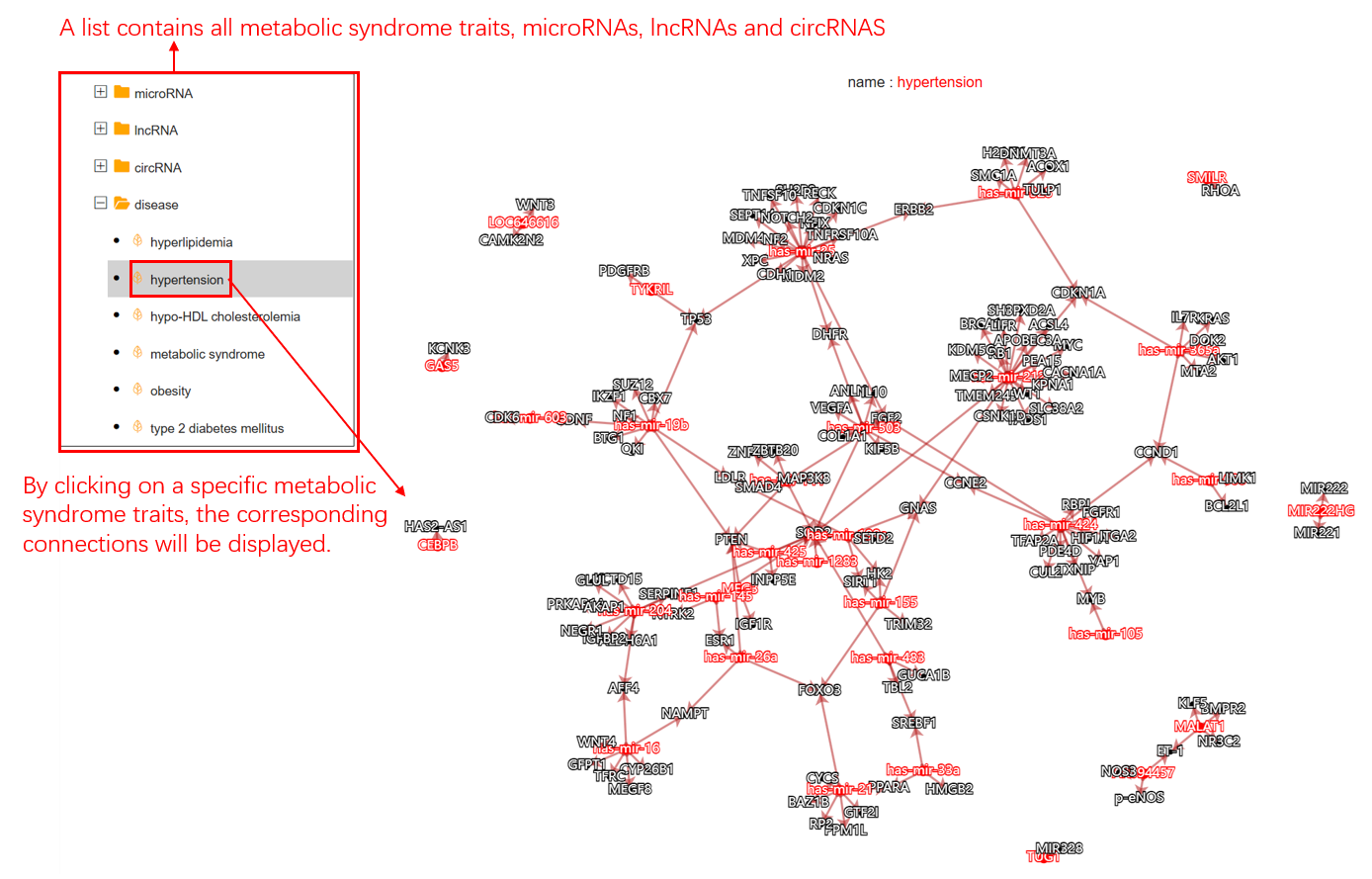 Figure 4. Interaction Page
Figure 4. Interaction Page